Content
- Consequences of the Election
- Examples of Mark to Market
- What is Credit Utilization Ratio and Why is It Important?
- Practical Mark-to-Market Accounting Example
- Mark to Market Accounting, How It Works, and Its Pros and Cons
- The Role of Mark-to-Market Accounting in the Current Financial Crisis
- What is mark-to-market in real estate?
Mark-to-market accounting can help banks and lending institutions determine the fair market of collectible collateral. In some instances, banks and other lenders will have to decide whether to extend the credit to those who aren’t able to pay them back. By knowing the actual market value, banks and lenders can make more informed decisions on whether it makes sense to extend a loan and by how much. Financial Accounting Standards Board eased the mark to market accounting rule. This suspension allowed banks to keep the values of the MBS on their books. If at the end of the day, the futures contract entered into goes down in value, the long margin account will be decreased and the short margin account increased to reflect the change in the value of the derivative.
- And, if this results in undermining public confidence in the reported accounting results, the proposed cure may further contribute to the crisis.
- Fair value accounting did not cause the current financial crisis, but the crisis may have been aggravated by common misperceptions about accounting standards.
- To meet the legitimate needs of both bankers and investors, regulatory officials should adopt new multidimensional approaches to financial reporting.
- The most infamous use of mark-to-market in this way was the Enron scandal.
- Mark to market involves adjusting the value of an asset to a value as determined by current market conditions.
- To accomplish this purpose, accounting must accurately portray the economic value of the assets held by a company.
- The mark-to-market accounting method may be inaccurate because the fair market value is subject to an agreement between two sides willing to complete a transaction.
This means that the trader with a short position in the future contact tends to benefit more from a fall in the value of the contract than the trader with a long position. However, daily mark to market settlements in future contracts continue until either of the parties closed his position and goes into a long contract. Traders can choose to use the mark-to-market rules, investors can’t. When reporting on Schedule D, both the limitations on capital losses and the wash sales rules continue to apply.
Consequences of the Election
However, as the financial crisis drags on and mortgage default rates continue to rise, bankers will face increasing pressure from their external auditors to recognize losses on financial assets as permanent. In this article, Pozen, the chairman of MFS Investment Management, dispels the myths about fair value accounting. For example, it’s untrue that most bank assets are marked to market—in 2008 just a third were. Nor is it true that under historical cost accounting, companies don’t have to acknowledge changes in market value; they’re required to record permanent impairments to assets. In the accounting industry, mark to market shows the current value of an asset, this is important in the compilation of financial statements for a fiscal year.
Why MTM is more than P&L?
Mark-to-Market is more accurate than Profit & Loss since it is adjusted regularly based on the stock price compared to during transactions only for P&L(e.g. purchase or sales).
Additionally, marketable securities would need to be decreased by the amount of the loss. For those securities that don’t have a maturity date, the investor intends to sell the securities sooner than they would normally be sold. The company reduced its net income in column F by 100% of the interest expense it incurred under a lending arrangement this period ($225,000). But it paid only a portion of its obligation in cash ($125,000) in column A, leaving the remainder ($100,000) in column C to be paid at a later date. Companies mitigate this risk by buying safer investment securities, and classifying a greater proportion of them as Held to Maturity (“HTM”) rather than Available for Sale (“AFS”). Fortunately for investors today, the SEC has taken big steps to protect investors from the kinds of risks they might have previously been unaware of. As investors, even the most knowledgeable of us may never be able to shield ourselves from every type of future accounting fraud.
Examples of Mark to Market
For a true day trader, this aspect of the election is of no significance. You don’t hold stocks at the end of the day, so you don’t hold stocks at the end of the year.
What is the problem with mark-to-market accounting?
Mark to market accounting forced banks to write down the values of their subprime securities. Now banks needed to lend less to make sure their liabilities weren't greater than their assets. Mark to market inflated the housing bubble and deflated home values during the decline.
The company would need to debit accounts receivable and credit sales revenue for the full amount of the sale. This method of accounting is also called fair value accounting.
What is Credit Utilization Ratio and Why is It Important?
The gain will increase the “mark to market and marketable securities.” In a case of a loss, marketable securities would need to be decreased by the loss amount, and the loss will also be recorded on the income statement as an unrealized loss. The exchange marks traders’ accounts daily to match the market value by settling the gains and losses resulting from fluctuations in the security’s value. If, for instance, the futures contract drops in value on day two, the long margin account will be decreased while the short margin account will increase to reflect the new value. In the opposite situation, the margin account of the long position holder will be increased while the short futures account will be decreased.

Neither the limitations on capital losses nor the wash sale rules apply to traders using the mark-to-market method of accounting. Mark-to-market accounting can change values on the balance sheet as market conditions change. In contrast, historical cost accounting, based on the past transactions, is simpler, more stable, and easier to perform, but does not represent current market value. Mark-to-market accounting can become volatile if market prices fluctuate greatly or change unpredictably. The Accountancy Journal has a nice piece that describes what went wrong with Enron and the role of mark-to-market accounting in hiding a lot of Enron’s corporate losses. Enron’s abuse of mark-to-market accounting basically consisted of two related practices. Second, Enron would record the total expected lifetime value of any given contract or project on its Balance Sheet rather than its value in that particular quarter.
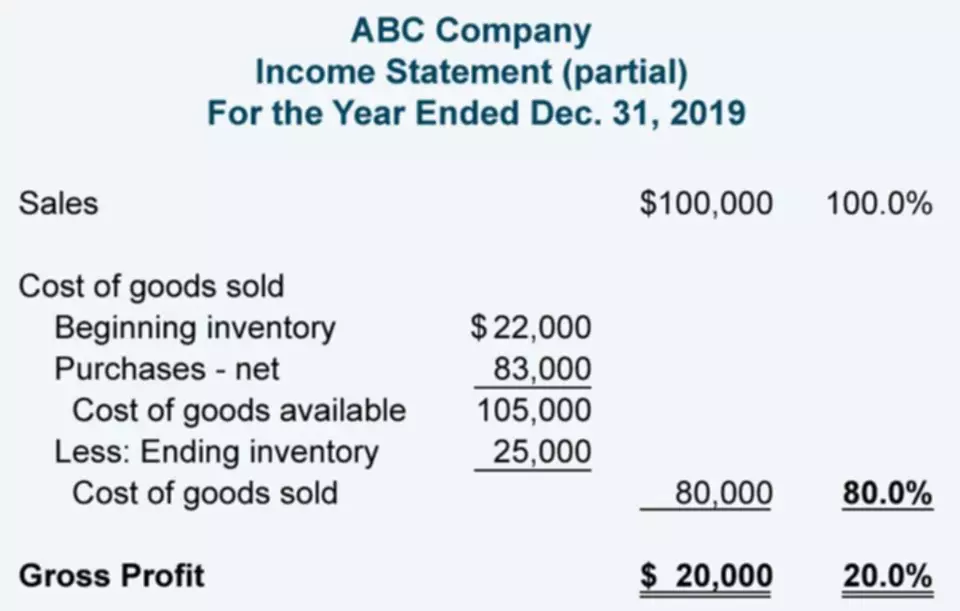
Practical Mark-to-Market Accounting Example
The most infamous use of mark-to-market in this way was the Enron scandal. Fair value accounting has been a part of Generally Accepted Accounting Principles in the United States since the early 1990s, and is now regarded as the “gold standard” in some circles.[which?

